Hip Replacement: Understanding the Procedure, Recovery & Benefits
pietro • November 9, 2022
Hip Replacement Surgery: Know about the Purpose, Procedure, and Recovery
Whether it’s because of old age, overuse, injury, or an accident, a growing number of people in the UK choose to get a hip replacement. Hip pain causes a tremendous amount of suffering only people affected and their loved ones can fully understand.
According to a report released by the NHS, the number of people aged 59 and younger who have undergone any form of procedure for hip replacement surgery went up by 76% in the last decade. The results are based on a comparison of cases registered between the periods 2004 to 2005, and 2014 to 2015.
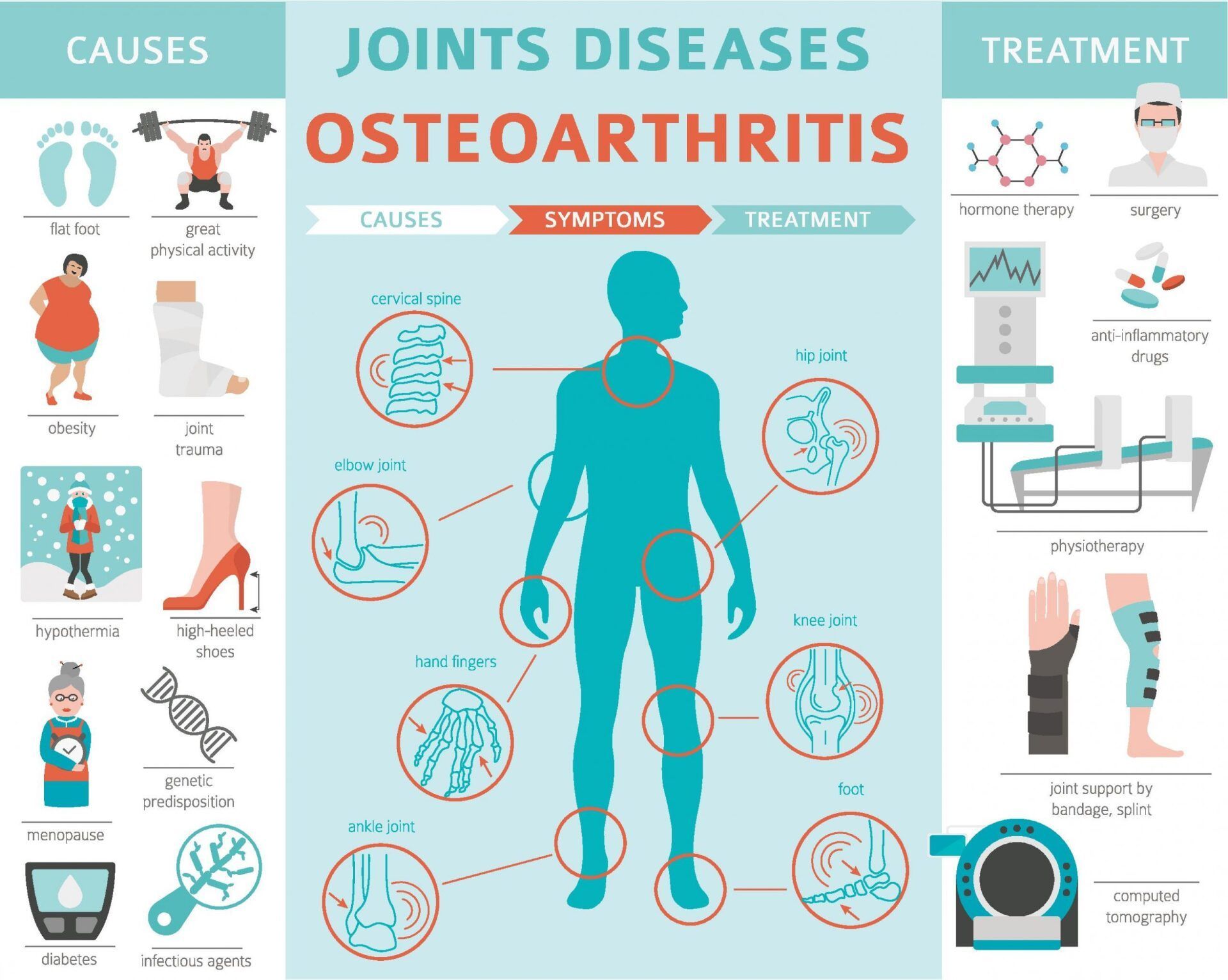
What’s Hip Replacement?
Hip Replacement is a major surgical procedure where the damaged hip joint is replaced by an artificial hip joint. This procedure is considered as a last resort not only because hip replacement cost requires a considerable sum of money, but also because healthcare providers are concerned with potential side effects.
Hip replacement procedures are considered only after other interventions, including pain medications, physical therapy, and using a cane, have been exhausted. As a prerequisite to surgery, patients complaining of pain on the hips typically need to undergo MRI to diagnose hip pain properly, ensuring that the benefits are greater than the risks.
Although hip replacement improves mobility and sensation of pain, the potential for repeat surgery is a consideration that healthcare providers want to avoid. Fortunately, based on a study conducted by the National Institute for Health Research, this hip pain treatment procedure now demonstrates that up to 50% of hip replacements stay intact for up to 25 years.
Do You Need Hip Replacement?
Pain on the hips can sometimes lead to debilitating conditions that make ordinary movements too challenging to even support activities such as walking and bathing. There are certain health conditions that increase your risk of damaging your hip joints, some of which are as follows:
- Sometimes termed osteoporosis arthritis in the hip, is one of the most common reasons causing the hip bone and joints to rub against each other, causing excruciating pain and stiffness of the back.
- Rheumatoid arthritis in the hip bone. This is the most prevalent type of arthritis characterized by chronic inflammation of the joints which causes bone-on-bone arthritis and worsen to adversely affect different parts of the body.
- Hip injury. Other than hip arthritis or bone cancer, accidents or slips resulting to massive injury of the hip bones and joints can also damage the cartilage and lead to pain and immobility of the hips.
- Avascular necrosis. This condition limits the blood supply to the hip joint resulting from a fracture which, in turn, further damages the hip joint, causing the bone to lose mass and die eventually.
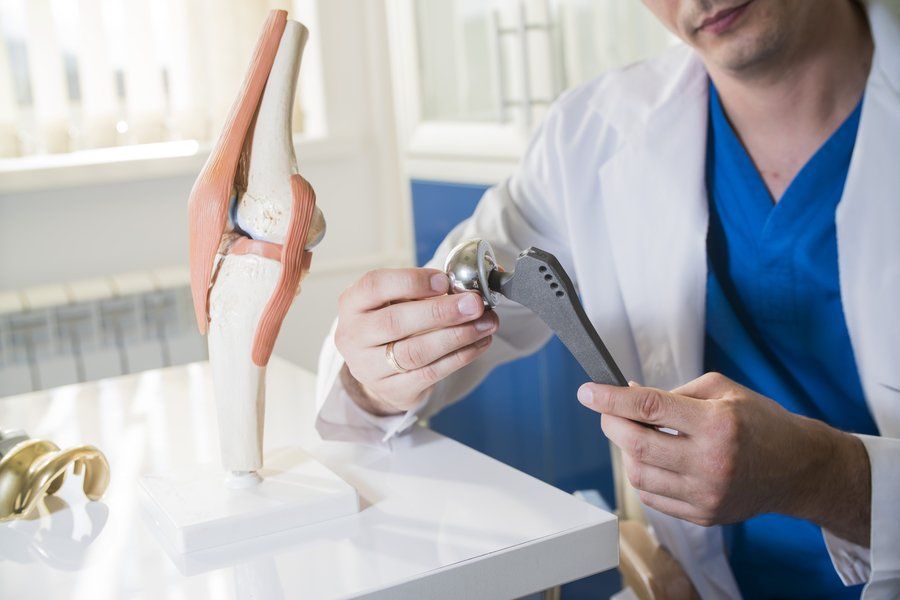
Hip Replacement Procedures
Based on the NHS, hip replacement surgery takes 1 to 2 hours to complete and typically requires general anesthesia. When this procedure is considered, healthcare providers generally make a recommendation from three hip replacement types:
- Hip Resurfacing. Considered as a minimally invasive procedure, this procedure involves removing only the damaged part of the hip bone, replacing it with a metal plate, and shorter recovery time. However, it also comes with risks such as causing damage to more tissues over time. The primary objective of hip resurfacing is to delay more massive hip replacement.
- Partial Hip Replacement. Medically termed as hip hemiarthroplasty, this procedure involves replacing the tip of the femur, also called “ball”, without replacing the acetabulum known as the “socket”.
- Total Hip Replacement. In contrast to partial hip replacement, this procedure involves replacing both ball and socket with a prosthetic then, inserting it to the hip stem. Higher hip surgery cost and longer recovery can be expected for this procedure.
PAA:
- What are the signs of needing a hip replacement?
Hip replacement is recommended to patients who:
- Complain of unbearable pain and stiffness on the hips
- Suffer from lack of immobility, and difficulty performing ordinary activities like bathing or getting out of bed due to chronic pain
- Have difficulty getting quality rest and sleep, and feel depression due to limitations to movement and social life
- What are hip implants made of?
Hip implants are generally made of metal-on-polyethylene, ceramic-on-ceramic, ceramic-on-polyethylene, and ceramic-on-metal. Each one has advantages and entails differences in risks over time. Metal-on-metal prosthetics are seldom used these days due to higher risks for causing further damage to bones and tissues on the hips and leaking metallic elements to the blood.
- Can I have both hips replaced at the same time?
Yes. In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend bilateral total hip replacement, particularly when degeneration of the bones and tissues are observed on both hips. You should, however, prepare to undergo longer recovery time and a more rigorous post-operation program that involves intense physical therapy as well as learning hip replacement exercises to avoid.
- What is the recovery time for a hip replacement?
Full recovery usually takes between 3 to 6 weeks, depending on the specific hip replacement procedure performed. Although, most patients are typically able to stand up and walk within 24 hours of undergoing the procedure. After hip replacement exercises are recommended to obtain stability and speed up recovery.
If you are a candidate for hip replacement or, considering one, talk to your physician about your options. Weigh out the benefits and risks of hip replacement with a health professional, and know for sure if this procedure is right for you.
References:
Roberts, M (2016). Rise in hip replacements for under 60s. BBC News Online. Link:
https://www.bbc.com/news/health-35699161
Access Date: 5 Apr 2020
National Institute for Health Research (2019). More than 50% of hip replacements appear to last 25 years. doi:
10.3310/signal-000781
Link:
https://evidence.nihr.ac.uk/alert/more-than-50-of-hip-replacements-appear-to-last-25-years/
Access Date: 5 Apr 2020
National Health Service. Overview. Hip Replacement. Link:
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/hip-replacement/
Access Date: 5 Apr 2020









